What is AI?
Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to perform tasks normally performed by humans. Whether it’s creating new content, powering chatbots, or predicting market trends, AI technology is rapidly transforming the way we live and work. No wonder there’s widespread AI adoption across all industries, with IBM reporting that 59% of organizations already exploring or deploying this technology are now accelerating their AI initiatives or investments.

How does AI work?
AI systems use a combination of data, algorithms, and computational power to emulate human cognitive abilities. Here’s a breakdown of how AI works:
1. Data collection and preprocessing
AI systems rely on vast amounts of data to learn and make informed decisions. That data can be collected from various sources, including sensors, databases, and the internet. It’s then preprocessed, which involves cleaning, organizing, and transforming the data into a format suitable for analysis.
2. Algorithms and machine learning
AI employs a variety of algorithms, with machine learning a key component. Machine learning algorithms enable systems to learn from the data and improve their performance over time. Supervised learning algorithms learn from labeled examples, while unsupervised learning algorithms identify patterns and structures in unlabeled data. Reinforcement learning algorithms use feedback from the environment to optimize decision-making.
3. Training data and inference
During the training phase, AI models are exposed to the preprocessed data to learn and adjust their internal parameters. This process involves optimization techniques like gradient descent, where the model iteratively adjusts its parameters to minimize errors or maximize performance. Once trained, the model is deployed for inference, where it applies its learned knowledge to new, unseen data to make predictions, classify objects, understand natural language, or perform other tasks.
Keep in mind that artificial intelligence is a broad field with various subfields and techniques, and the specific workings can vary depending on the approach, whether it’s deep learning, natural language processing (NLP), or another AI methodology.
Why is AI important?
AI’s importance lies in its potential to revolutionize industries, achieve greater efficiency, and enhance decision-making processes.
- Automation and efficiency: AI technologies enable automation of repetitive and mundane tasks, leading to increased efficiency and productivity. With AI-generated content, for example, you take over time-consuming and routine operations, freeing up human resources to focus on more complex endeavors. This type of automation has the potential to streamline processes across various industries, reducing costs and improving accuracy.
- Improved decision-making: AI can analyze vast amounts of data, extract valuable insights, and make data-driven predictions and decisions, including more accurate diagnoses and better investment strategies. This ability to process and interpret complex data sets enables AI systems to identify patterns, detect anomalies, and generate actionable recommendations. Take AI summarization, for example. By quickly summarizing complex reports or research papers, AI helps us grasp key information efficiently. This allows decision-makers to focus on the most relevant details and make informed choices without getting bogged down with information overload.
- Advancements in various fields: AI drives innovations in healthcare, transportation, education, agriculture, and more. In healthcare, AI is used for medical imaging analysis, drug discovery, and personalized treatment plans. In transportation, AI contributes to the development of autonomous vehicles, optimizing traffic management, and enhancing logistics operations. AI-powered education platforms offer personalized learning experiences and adaptive tutoring. These advancements have the potential to improve the quality of life, enhance safety, and solve complex problems.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of AI?
Like any powerful technology, AI brings advantages and disadvantages depending on the specific application and implementation.
AI impact | Advantages of AI | Disadvantages of AI |
Economic impact | Automation of repetitive tasks, increasing efficiency and productivity | Potential job displacement and impact on employment opportunities |
Decision making | Assistance in complex problem solving and improved decision-making through data analysis and prediction | Lack of transparency and interpretability in AI decisions |
Data management | Ability to handle and process large amounts of data quickly and accurately | Reliance on data quality and potential biases in training |
Resource management | Potential for resource optimization and cost reduction | The need to ensure employees are trained on the latest technologies |
Personalization | Customization of experiences and services | Potential for loss of privacy, as personalized experiences often require data collection about users |
Safety, privacy, and security | Support for dangerous and high-risk tasks, minimizing human exposure to harm | Ethical dilemmas regarding accountability and responsibility |
Discover how to measure the impact of AI on your business.
What are the types of artificial intelligence?
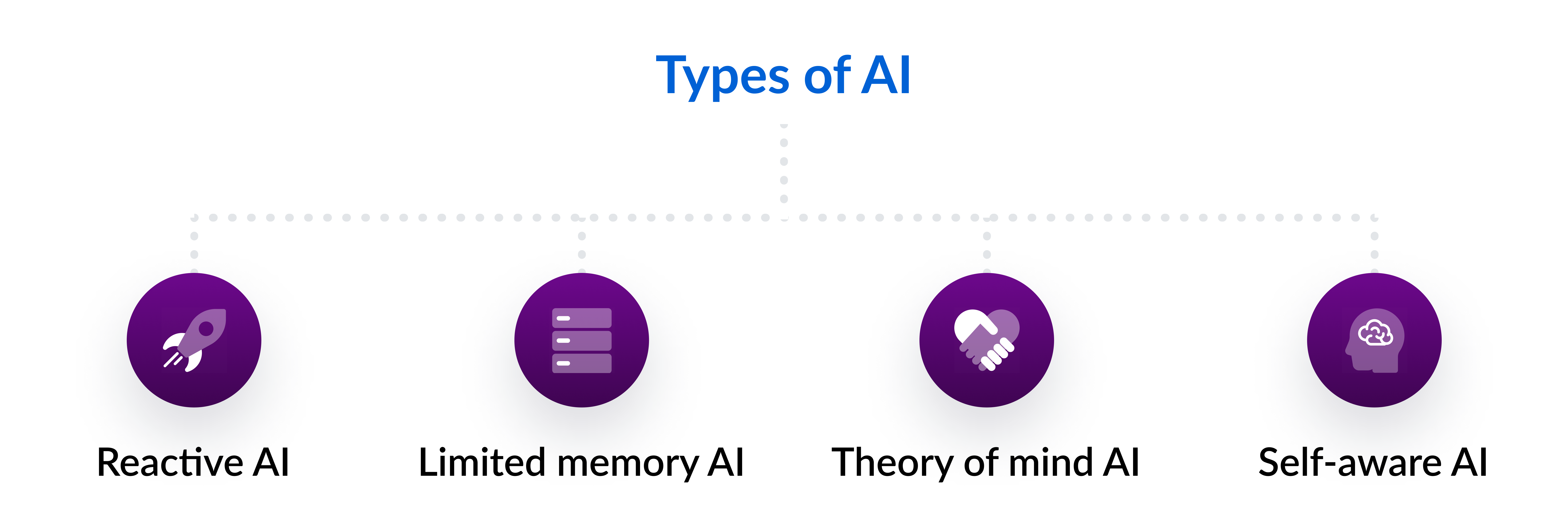
There are seven types of AI, but let’s look at the four most common in enterprise use cases.
1. Reactive AI
Reactive AI systems operate purely based on the current input without any memory or ability to form past experiences. They do not have the capability to learn from previous interactions or make future predictions. Reactive AI systems are designed to react to specific situations and produce predefined responses. They excel at tasks that require real-time processing and quick decision-making, such as playing chess or driving a car.
2. Limited memory AI
Limited memory AI builds upon reactive AI by incorporating memory elements. These AI systems can retain a limited amount of past information to make informed decisions in the present. They utilize historical data to enhance their performance, but their memory is typically short term. Limited memory AI is useful in tasks that require some context awareness, such as autonomous navigation or recommendation systems.
Generative AI is a specific subset of limited memory AI that leverages a vast amount of training data to learn patterns and structures in order to generate novel outputs. This capability makes them particularly adept at tasks like creative writing, image generation, and content discovery.
3. Theory of mind AI
Theory of mind AI aims to develop machines that can understand and attribute mental states to themselves and others. This theoretical level of AI would involve understanding emotions, beliefs, intentions, and desires, allowing machines to interact more naturally with humans and infer their perspectives. Theory of mind AI is still largely a theoretical concept and an active area of research.
4. Self-aware AI
Self-aware AI is the hypothetical level of AI where machines would possess consciousness and self-awareness similar to human beings. They would have a sense of their own existence, emotions, and thoughts. Self-aware AI goes beyond understanding the external world and focuses on internal experiences.
AI tools and services
There is a wide range of AI tools and services that cater to different needs and applications. Here are some popular options.
- Box AI: This suite of capabilities natively integrates advanced generative AI models into Box. With Box AI, you can unlock the full potential of your unstructured data: asking questions about multiple documents at once, generating new content in seconds, extracting valuable metadata, automating workflows, enhancing security, and more. Box AI makes it possible for enterprises to leverage cutting-edge technology while keeping their data secure.
- TensorFlow: This open-source machine learning framework — developed by Google — provides a comprehensive ecosystem for building and deploying AI models, including deep learning models. TensorFlow supports various platforms and has extensive community support.
- PyTorch: This is another open-source deep learning framework widely used in research and industry. It offers dynamic computational graphs, making it flexible for model development and experimentation. PyTorch is known for its user-friendly interface and strong community engagement.
- Microsoft Azure Cognitive Services: This suite of AI services provides ready-to-use APIs for computer vision, speech recognition, natural language processing, and more. It allows developers to easily integrate AI capabilities into their applications without needing to build everything from scratch.
- Google Cloud AI Platform: Google offers a range of AI tools and services to build, train, and deploy machine learning models. It provides access to pre-trained models, custom model-development capabilities, and distributed training options. The platform supports popular frameworks like TensorFlow and scikit-learn.
- IBM Watson: This AI platform offers a wide array of services, including natural language processing, chatbots, image recognition, and predictive analytics. Watson’s APIs and tools enable developers to leverage AI capabilities in their applications.
- Amazon AI Services: Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers a suite of AI services, collectively known as Amazon AI. They include Amazon Rekognition for image and video analysis, Amazon Polly for text-to-speech conversion, Amazon Lex for building chatbots, and Amazon Comprehend for natural language processing tasks.
- OpenAI GPT: OpenAI’s Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT) models are powerful language models that can generate human-like text. Developers can use OpenAI’s API to integrate GPT models into their applications for tasks such as text generation, language translation, and conversation generation.
The choice of tool or service depends on specific requirements, programming languages, platforms, and the complexity of the AI tasks at hand.
Ethics of AI
AI raises important ethical considerations when it comes to:
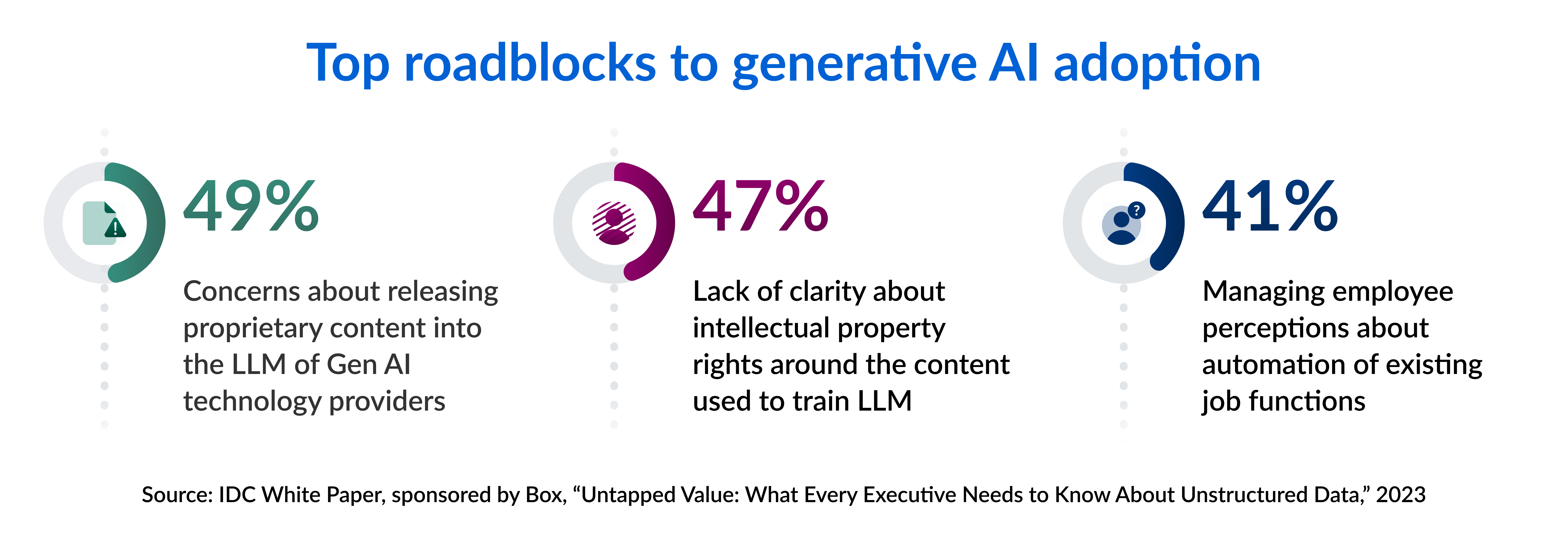
- Privacy and data usage: AI systems often require access to vast amounts of data to train and make accurate predictions. The collection, storage, and use of personal data raise concerns about privacy, consent, and potential misuse. Case in point: when asked about the biggest roadblocks to GenAI adoption, 49% of respondents in a Box-sponsored IDC study cited concerns about releasing their organization’s proprietary content into the large language models of AI providers. For this reason, it’s essential to establish robust data protection policies, ensure transparency in data-handling practices, and seek solutions with ethical AI principles.
- Bias and fairness: AI systems can inherit biases present in the data used for training. Biases related to race, gender, or other protected attributes can lead to unfair outcomes and discrimination. Efforts should be made to mitigate bias in data collection, AI algorithm design, and decision-making processes to ensure fairness and prevent perpetuating societal biases.
- Accountability and transparency: AI systems often operate as “black boxes,” making it difficult to understand how decisions are reached. Lack of transparency can undermine trust and hinder accountability. Make efforts to ensure that AI systems are explainable and provide clear reasoning for their outputs, particularly in critical domains like healthcare and criminal justice.
- Job displacement and economic impact: The automation capabilities of AI raise concerns about job displacement and the impact on the workforce. While AI can also create new job opportunities, it’s crucial to address the potential economic inequalities and ensure proper training and reskilling programs to support affected individuals.
- Safety and security: In the case of autonomous vehicles or critical infrastructure control systems, ensuring the reliability, robustness, and security of AI systems is important to prevent accidents, malicious security threats, or unintended consequences.
- Social impacts and inequality: AI can exacerbate existing social inequalities if not implemented and deployed thoughtfully. Access to AI technologies, biases in AI algorithms, and the digital divide can all contribute to social exclusion and disadvantage certain groups. Efforts should be made to ensure equitable access, minimize disparities, and promote inclusive AI development and deployment.
Addressing these ethical concerns requires collaboration among policymakers, industry leaders, researchers, and society as a whole. It’s essential to:
- Build an AI strategy for your enterprise
- Establish frameworks, guidelines, and regulations to govern AI use
- Promote responsible AI development
- Prioritize ethical considerations in the design, deployment, and governance of AI systems
How is AI used today?
Let’s review prominent AI applications.
- Healthcare: AI and machine learning algorithms can help detect patterns in medical images, predict patient outcomes, and assist in personalized medicine. AI is also used for drug discovery, genomics research, and virtual health assistants.
- E-commerce and recommendation systems: AI provides personalized product recommendations based on user preferences and behaviors. This enhances the shopping experience and increases customer engagement. AI is also used in retail for demand forecasting and inventory management.
- Autonomous vehicles: Computer vision and machine learning algorithms enable vehicles to perceive the environment, recognize objects, and make real-time decisions for safe navigation. Companies like Tesla, Waymo, and Uber are actively researching and implementing AI in autonomous driving technologies.
- Virtual assistants: Apple’s Siri, Amazon’s Alexa, and Google Assistant all use natural language processing and machine learning algorithms to understand and respond to user voice commands. They assist with tasks such as setting reminders, providing weather updates, playing music, and controlling smart home devices.
- Financial services: AI is extensively used in the finance industry for fraud detection, risk assessment, and algorithmic trading. Machine learning models analyze large volumes of transaction data to identify anomalies and patterns that could indicate fraudulent activities. AI also helps in credit scoring and personalized financial recommendations.
- Customer service and chatbots: Natural language processing and machine learning algorithms enable chatbots to understand and respond to customer queries, providing instant assistance and personalized recommendations.
- Cybersecurity: Machine learning models analyze network traffic, user behavior, and system logs to identify patterns and anomalies indicative of malicious activities. AI-powered systems can automatically respond to attacks and adapt to evolving security threats.

Use AI to get the most from your content
With one secure, intelligent platform for all your content, Box enables you to manage the entire content lifecycle: file creation, co-editing, sharing, e-signature, classification, retention, and so much more. We make it easy for you to collaborate on content with anyone, both inside and outside your organization.
With Box AI, we integrate generative AI models into our Intelligent Content Management platform. . You can automate workflows, improve information governance, and gain insights from content, even without in-house machine learning expertise.
As always, frictionless, enterprise-grade security and compliance are built into our DNA, so you get total peace of mind that your content is protected. And with 1,500+ seamless integrations — as well as a range of native capabilities, like Box Sign and Box Canvas — the leading Intelligent Content Management platform provides a single content layer that ensures your teams can work the way they want.
Contact us today, and explore what you can do with Box.

**While we maintain our steadfast commitment to offering products and services with best-in-class privacy, security, and compliance, the information provided in this blog post is not intended to constitute legal advice. We strongly encourage prospective and current customers to perform their own due diligence when assessing compliance with applicable laws.